
Most chemical materials are used under ambient conditions, which is the most important aspect of chemistry for us humans. HistoryĬhemistry is the art, craft, and science of modifying matter, hopefully improving materials for the benefits of humanity. The chemical ordinal number Z of an element in the Periodic Table is equal to the physical cardinal number of Z electrons in the neutral atom around its nucleus of the same charge number Z. Common Periodic Tables are mnemonics for the trends of the meta-properties of the chemical elements under common conditions, useful in practical chemistry and in chemical education. The IUPAC suggests using the word ‘element’ as a homonym for both. The many allotropic ‘elementary substances’ (carbon as diamond, graphite, graphenes, nanotubes, fullerenes, etc., for example) are composed of a single ‘abstract element’ only. The Emergence of Naturally 2-Dimensional Tables of Chemical ElementsĬhemical elements are the basic, abstract entities conserved in chemical transformations of real substances. The general conclusions are presented in the last, summarizing section. Before the (sub)sections we present the inferences according to our own viewpoints, as take-home messages in italicized text. These points are illustrated with examples. Therefore, we analyze the following points: the general principles of empirical periodicity their objective physical background deviations from expected periodicity misrepresentations or misinterpretations of periodicity and unexpected trends in chemistry. Some compounds or chemical preparation methods were thought to be non-existent or impossible. Under such circumstances, misunderstandings of the Periodic Table happen easily, and unexpected chemistry is overlooked. Thus, modern chemistry developed not only along the lines of easily available and practically useful chemicals, but also with effectively blinkered expectations according to the Periodic Table ( Keserü et al., 2014 Pye et al., 2017 Llanos et al., 2019 Restrepo, 2019a, b). Then, during the past hundred years, students learned general and inorganic chemistry, and later practiced these through Periodic-Table colored glasses, rationalized by atomic structure theory.

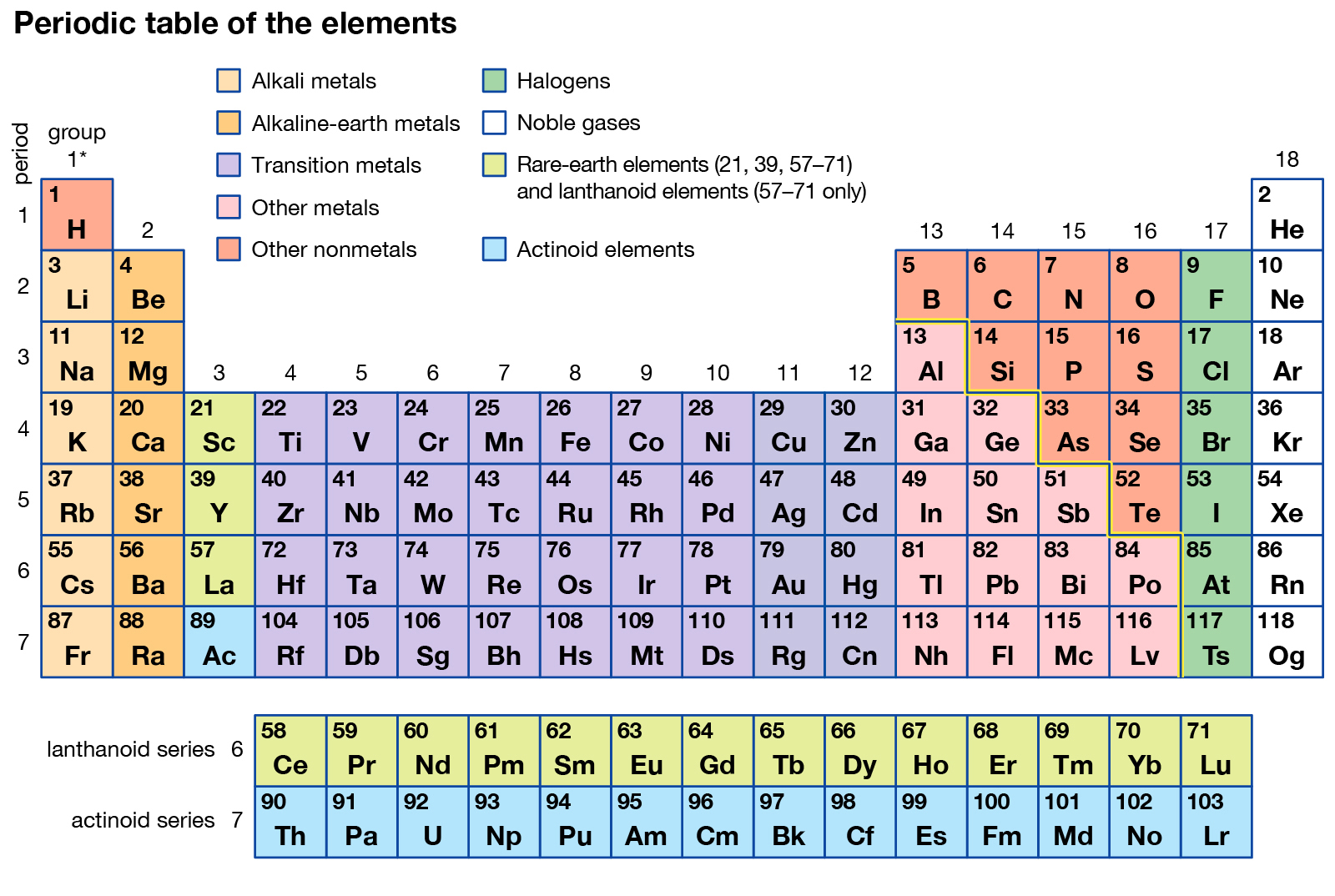
Within half a century, with more or less delay depending on the author, Periodic Tables of elements entered most chemistry books and lecture rooms ( Kaji et al., 2015 Robinson, 2019). They addressed this need with the help of two-dimensional tables for groups of elements. Two to one-and-half centuries ago, authors of chemistry books and chemistry teachers such as Leopold Gmelin ( Gmelin, 1843), Lothar Meyer ( Meyer, 1864), Dmitri Mendeleev ( Mendeleev, 1869b) and Viktor von Richter ( Von Richter, 1875) felt the need for an ordered arrangement of the increasing number of elements. The combination of experimental data and theoretical insight supports a more nuanced understanding of complex periodic trends and non-periodic phenomena. While it is essential that Periodic Tables display important trends in element chemistry we need to keep our eyes open for unexpected chemical behavior in ambient, near ambient, or unusual conditions.
Periodic table chemistry class free#
Simplified, artistic, or economic tables are relevant to educational and cultural fields, while practicing chemists profit more from “chemical tables of chemical elements.” Such tables should incorporate four aspects: (i) typical valence electron configurations of bonded atoms in chemical compounds (instead of the common but chemically atypical ground states of free atoms in physical vacuum) (ii) at least three basic chemical properties ( valence number, size, and energy of the valence shells), their joint variation across the elements showing principal and secondary periodicity (iii) elements in which the (sp) 8, (d) 10, and (f) 14 valence shells become closed and inert under ambient chemical conditions, thereby determining the “fix-points” of chemical periodicity (iv) peculiar elements at the top and at the bottom of the Periodic Table. Such tables have been designed with the aim of either classifying real chemical substances or emphasizing formal and aesthetic concepts. To this end, a graphical display of the chemical properties of the elements, in the form of a Periodic Table, is the helpful tool. Comprehensive overviews of the chemistry of the elements and their compounds are needed in chemical science. The chemical elements are the “conserved principles” or “kernels” of chemistry that are retained when substances are altered. 4Department of Chemistry, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China.3Department of Chemistry, University of Siegen, Siegen, Germany.2Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia.1Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
